# DataLoader 中 pin_memory 的作用
難度:易
# 什麼時候該使用
在 Dataset 中讀取資料到 CPU (RAM) 上,然後在訓練階段將資料轉移到 GPU 上。
# 什麼時候沒有用
在 Dataset 中已經讀取資料到 GPU (vRAM) 上,然後在訓練階段不會將資料轉移到 GPU 上。重點是資料轉移的過程,沒有資料轉移就不會有額外消耗。
# 原理
Pinned 的意思是 page-locked(鎖定分頁的)。在 CPU 中,記憶體預設都是 pageable(可分頁的記憶體)。但是在可分頁記憶體中的資料無法直接傳入 GPU 的記憶體中,傳入前必須先進行鎖定。在 NVIDIA blog (opens new window) 中這麼說:
Host (CPU) data allocations are pageable by default. The GPU cannot access data directly from pageable host memory, so when a data transfer from pageable host memory to device memory is invoked, the CUDA driver must first allocate a temporary page-locked, or “pinned”, host array, copy the host data to the pinned array, and then transfer the data from the pinned array to device memory, as illustrated below.
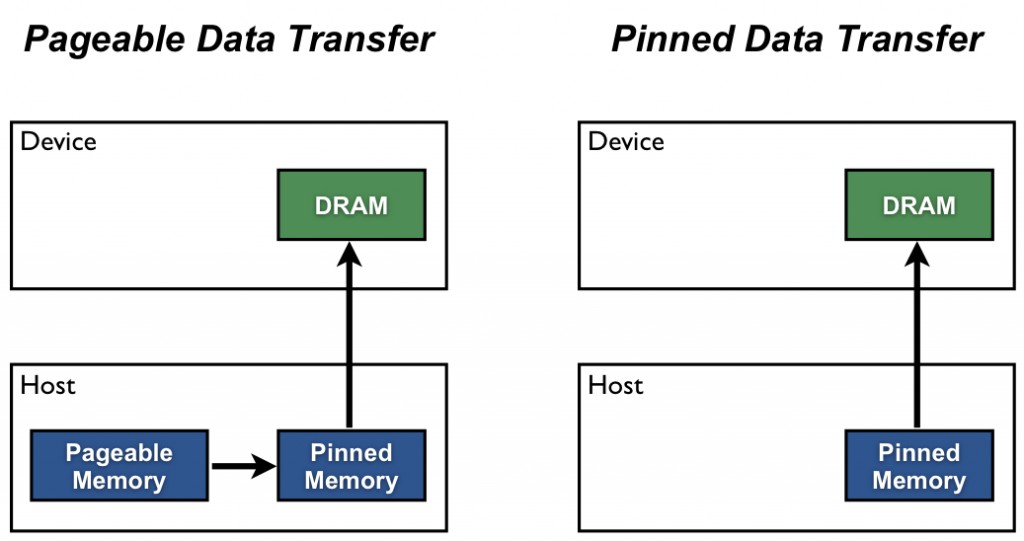
所以設定 pin_memory=True 就只是先傳入鎖定分頁的記憶體上,之後要搬到 GPU 就可以直接搬。在 DataLoader 中意義更重大,設定好就不會每次讀取資料都要鎖定。
# 如何在 DataLoader 中使用
通常是直接下參數 pin_memory=True,它會辨識 Dataset 回傳的物件中,哪些是屬於 Tensor 型別的資料,還有「dict 或是 iterable 的容器物件中,包含 Tensor 型別的資料」,把這些資料傳入 pinned memory。如果是自製的資料型別,就必須自己寫一個包含 pin_memory(self) 函式的類別,傳入參數 collate_fn,來指定設定 pin_memory=True 時該有的行為。以下是官網的範例:
class SimpleCustomBatch:
def __init__(self, data):
transposed_data = list(zip(*data))
self.inp = torch.stack(transposed_data[0], 0)
self.tgt = torch.stack(transposed_data[1], 0)
# custom memory pinning method on custom type
def pin_memory(self):
self.inp = self.inp.pin_memory()
self.tgt = self.tgt.pin_memory()
return self
def collate_wrapper(batch):
return SimpleCustomBatch(batch)
inps = torch.arange(10 * 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(10, 5)
tgts = torch.arange(10 * 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(10, 5)
dataset = TensorDataset(inps, tgts)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=2, collate_fn=collate_wrapper,
pin_memory=True)
for batch_ndx, sample in enumerate(loader):
print(sample.inp.is_pinned())
print(sample.tgt.is_pinned())
從範例中可以看到,DataLoader 在取出一個 batch 的資料時,會去呼叫它的 pin_memory() 函式。所以如果自製的 Batch 型別並非上述的容器物件,必須自己實作 pin_memory()。
# 參考資料
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#memory-pinning (opens new window)
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#cuda-memory-pinning (opens new window)
- https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/how-optimize-data-transfers-cuda-cc/ (opens new window)
- https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/when-to-set-pin-memory-to-true/19723 (opens new window)
← 前言