# Replace Constructors with Creation Methods
以「目的清楚、返回物件實體」的 Creation Method 取代建構式。
# 動機
建構式的問題:
- 客戶必須研究建構式的參數,在 source code 中摸索
- 建構式無法傳達目的
- 如果 class 已經存在相同簽名(signature)的建構式,則無法新增新的建構式
- 不再用到的建構式還苟延殘喘
Creation Method vs. Factory Method
Creation Method: 用來創建 class 物件實體的 static/nonstatic 函式。 意味著每個 Factory Method 都是 Creation Method,反之不必然成立。
優點
- 比 constructors 更能有效表達可獲得哪一種物件實體。
- 突破 constructors 的限制。
- 更容易找出未使用的 creation code。
缺點
- 如果你的 classes 有些使用 new 有些使用 Creation Method,客戶必須學習如何使用不同的 classes 來創建。
# 作法
在重構之前,先找出 catch-all 的建構式:一個功能完整的建構式,其他建構式會把工作委託給它。 如果沒有 catch-all,可以實施 Chain Constructor 做出一個。
- 找出一個「為了創建某種性質的實體而呼叫 class 的建構式(假設是
Ctor1)」的客戶碼。對這個建構式實施 Extract Method [F],建立起一個 public static 函式。這個新函式是個 Creation Method。 再實施 Move Method [F] 將 Creation Method 移至內涵建構式Ctor1的那個 class 中。- 編譯並測試。
- 找出建構式
Ctor1(其所創建的實體與 Creation Method 創建的實體是同一種)所有呼叫者,讓它們改而呼叫 Creation Method。- 編譯並測試。
- 如果上述建構式
Ctor1呼叫另一個建構式Ctor2,就讓 Creation Method 轉而呼叫Ctor2。 透過「將建構式 inline 化」進行這個步驟。(類似 Inline Method [F])- 編譯並測試
- 對任何想要轉換成 Creation Method 的建構式,重複步驟 1--3。
- 如果這些 class 建構式沒有 class 之外的呼叫者,把它們設為 non-public。
- 編譯
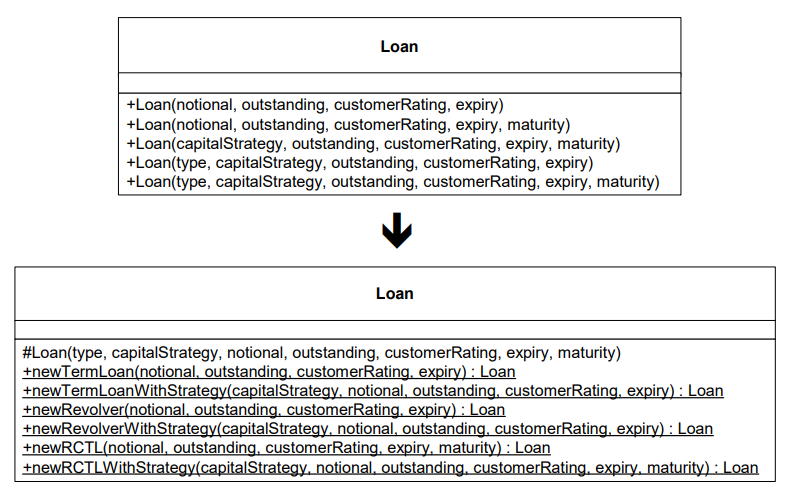
# 範例
public class Loan {
private static String TERM_LOAN = “TL”;
private static String REVOLVER = “RC”;
private static String RCTL = “RCTL”;
private String type;
private CapitalStrategy strategy;
private float notional;
private float outstanding;
private int customerRating;
private Date maturity;
private Date expiry;
public Loan(float notional, float outstanding, int customerRating, Date expiry) {
this(TERM_LOAN, new TermROC(), notional, outstanding,
customerRating, expiry, null);
}
public Loan(float notional, float outstanding, int customerRating, Date expiry,
Date maturity) {
this(RCTL, new RevolvingTermROC(), notional, outstanding, customerRating,
expiry, maturity);
}
public Loan(CapitalStrategy strategy, float notional, float outstanding,
int customerRating, Date expiry, Date maturity) {
this(RCTL, strategy, notional, outstanding, customerRating,
expiry, maturity);
}
public Loan(String type, CapitalStrategy strategy, float notional,
float outstanding, int customerRating, Date expiry) {
this(type, strategy, notional, outstanding, customerRating, expiry, null);
}
public Loan(String type, CapitalStrategy strategy, float notional,
float outstanding, int customerRating, Date expiry, Date maturity) {
this.type = type;
this.strategy = strategy;
this.notional = notional;
this.outstanding = outstanding;
this.customerRating = customerRating;
this.expiry = expiry;
if (RCTL.equals(type))
this.maturity = maturity;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
Loan class 有七種貸款方式,這邊只討論其中三種:
- loan
- revolver
- RCTL
為何不把 Loan 當作 superclass,其他種類當作 subclass?
- 區別不同種類的貸款不是取決於欄位,而是根據數值。
不想為了支援定期貸款的三種不同計算方式產生三種 class。
較簡單的做法是支援一個
Loanclass 並針對定期貸款有三種不同 Strategy class。(見 Replace Conditional Logic with Strategy (129) ) - 使用
Loan實體的應用程式有「轉換貸款種類」的需求。 為了轉換工作容易些,我們希望只改變Loan實體的少量欄位,而不是將某個Loansubclass 完全改成另一個。
# 開始重構
找出客戶碼,在這裡是測試程式。
public class CapitalCalculationTests... public void testTermLoanNoPayments() { ... Loan termLoan = new Loan(commitment, riskRating, maturity); ... }1
2
3
4
5
6使用 Extract Method [F] 成
createTermLoan()Loan termLoan = createTermLoan(commitment, riskRating, maturity) ;1public static Loan createTermLoan(double commitment, int riskRating, Date maturity) { return new Loan(commitment, riskRating, maturity); }1
2
3接下來在 creation method
createTermLoan()實施 Move Method 到Loan內:public class Loan... public static Loan createTermLoan(double commitment, int riskRating, Date maturity) { return new Loan(commitment, riskRating, maturity); } public class CapitalCalculationTest... public void testTermLoanNoPayments() { ... Loan termLoan = Loan.createTermLoan(commitment, riskRating, maturity); ... }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11- 編譯並測試,確保正常。
找出
createTermLoan()呼叫的那個建構式所有的呼叫者,把它們改成createTermLoan()。createTermLoan()是上述建構式的唯一呼叫者。 由於這個建構式被連結到其他建構式,我們使用 Inline Method [F](在這裡應該稱為 inline constructor)把連結解除。public Loan(double commitment, int riskRating, Date maturity) { this(commitment, 0.00, riskRating, maturity, null); }1
2
3public class Loan... ... // 移除 public Loan(double commitment, int riskRating, Date maturity) public static Loan createTermLoan(double commitment, int riskRating, Date maturity) { return new Loan(commitment, 0.00, riskRating, maturity, null); }1
2
3
4
5- 編譯並測試
重複 1--3。例如以下
public class CapitalCalculationTest... public void testTermLoanWithRiskAdjustedCapitalStrategy() { ... Loan termLoan = new Loan(riskAdjustedCapitalStrategy, commitment, outstanding, riskRating, maturity, null); ... }1
2
3
4
5
6傳
null是不好的習慣,其降低可讀性,所以讓它們改用 creation method。public class CapitalCalculationTest... public void testTermLoanWithRiskAdjustedCapitalStrategy() { ... Loan termLoan = Loan.createTermLoan (riskAdjustedCapitalStrategy, commitment, outstanding, riskRating, maturity); ... } public class Loan... public static Loan createTermLoan(double commitment, int riskRating, Date maturity) { return new Loan(commitment, 0.00, riskRating, maturity, null); } public static Loan createTermLoan(CapitalStrategy riskAdjustedCapitalStrategy, double commitment, double outstanding, int riskRating, Date maturity) { return new Loan(riskAdjustedCapitalStrategy, commitment, outstanding, riskRating, maturity, null); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15為什麼選擇 overload
createTermLoan()而不再寫一個 create method 例如createTermLoanWithStrategy()? 因為CapitalStrategy參數的存在已經可以充分表達這兩個createTermLoan()的版本不同。 ...(略)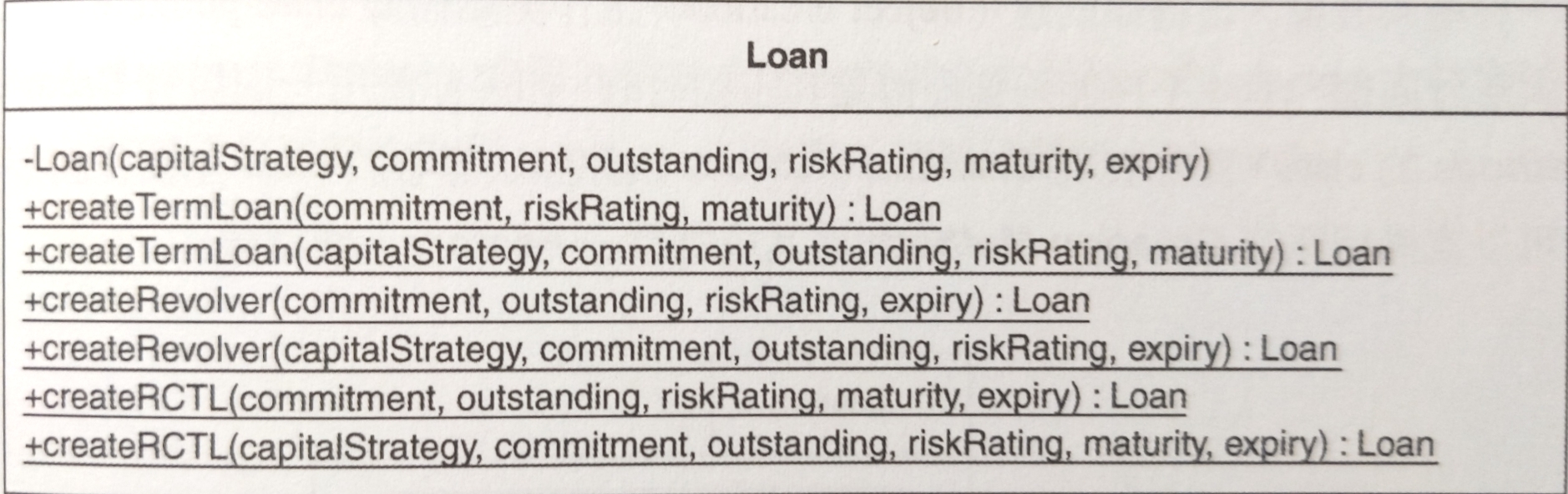
改變
Loan可視性(visibility),改成 private,因為它已經沒有外部呼叫者了。public class Loan... private Loan(CapitalStrategy capitalStrategy, double commitment, double outstanding, int riskRating, Date maturity, Date expiry) ...1
2
3
# 變種 Variations
# 參數化的 Creation Method
可能使用 Replace Constructors with Creation Methods 會產生數十種 Creation Method 來負責 class 每一種物件設定。為此可能決定不使用這項重構。
- 將最常見的設定撰寫 Creation Method 並在周圍留下 public constructor 以便處理其他狀況。
- 運用參數的變化來降低 Creation Method 的數量。
# Extract Factory
當一個 class 太多 Creation Method 會混淆 class 的主要任務,可以重構 Creation Method 成為單一 Factory
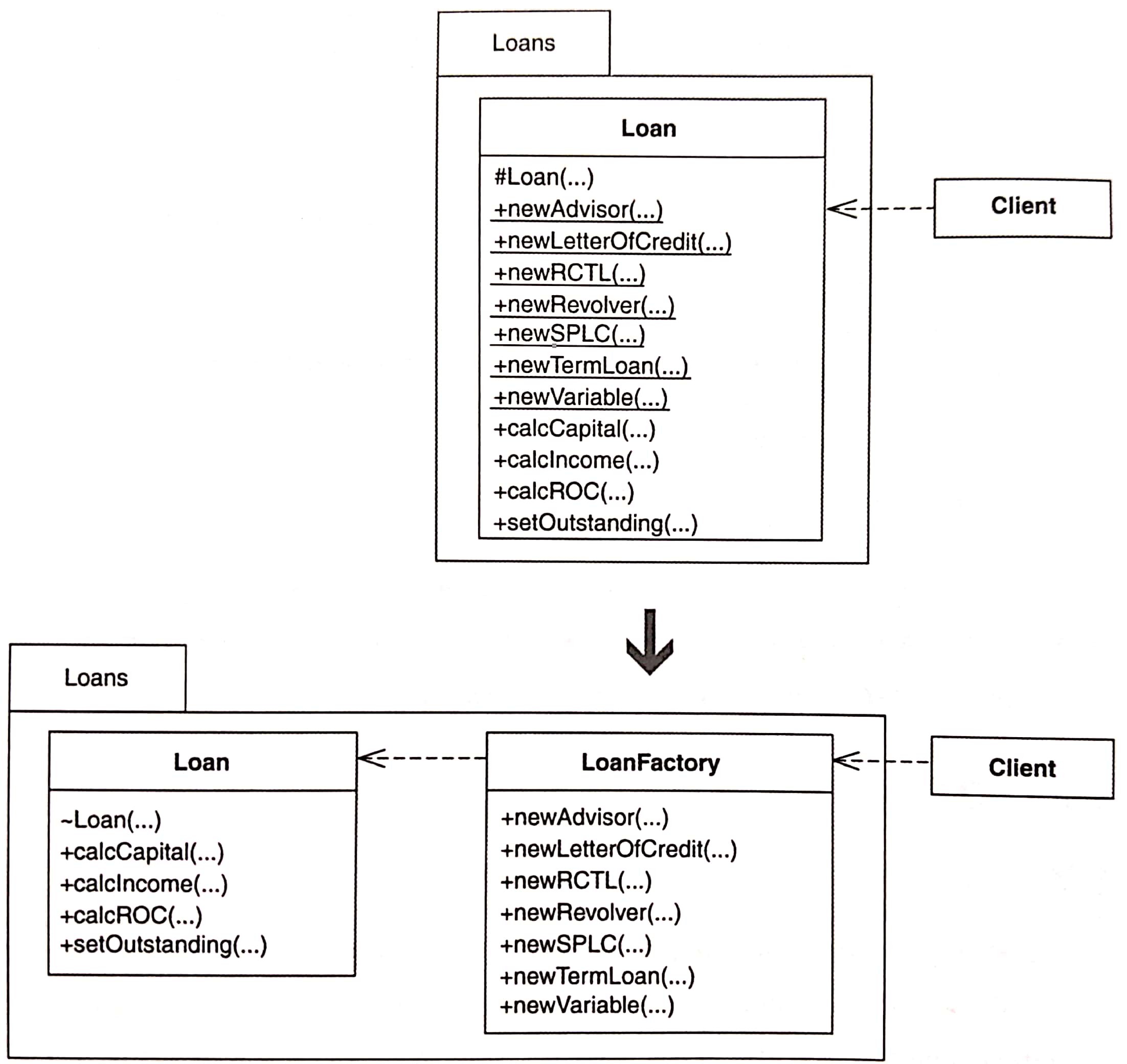
注意,這裡的 Factory 不是 Abstract Factory [DP]。Abstract Factory 可以在執行期被替換,Factory 比較沒那麼複雜,且通常實作成單一 class,不會使用繼承。