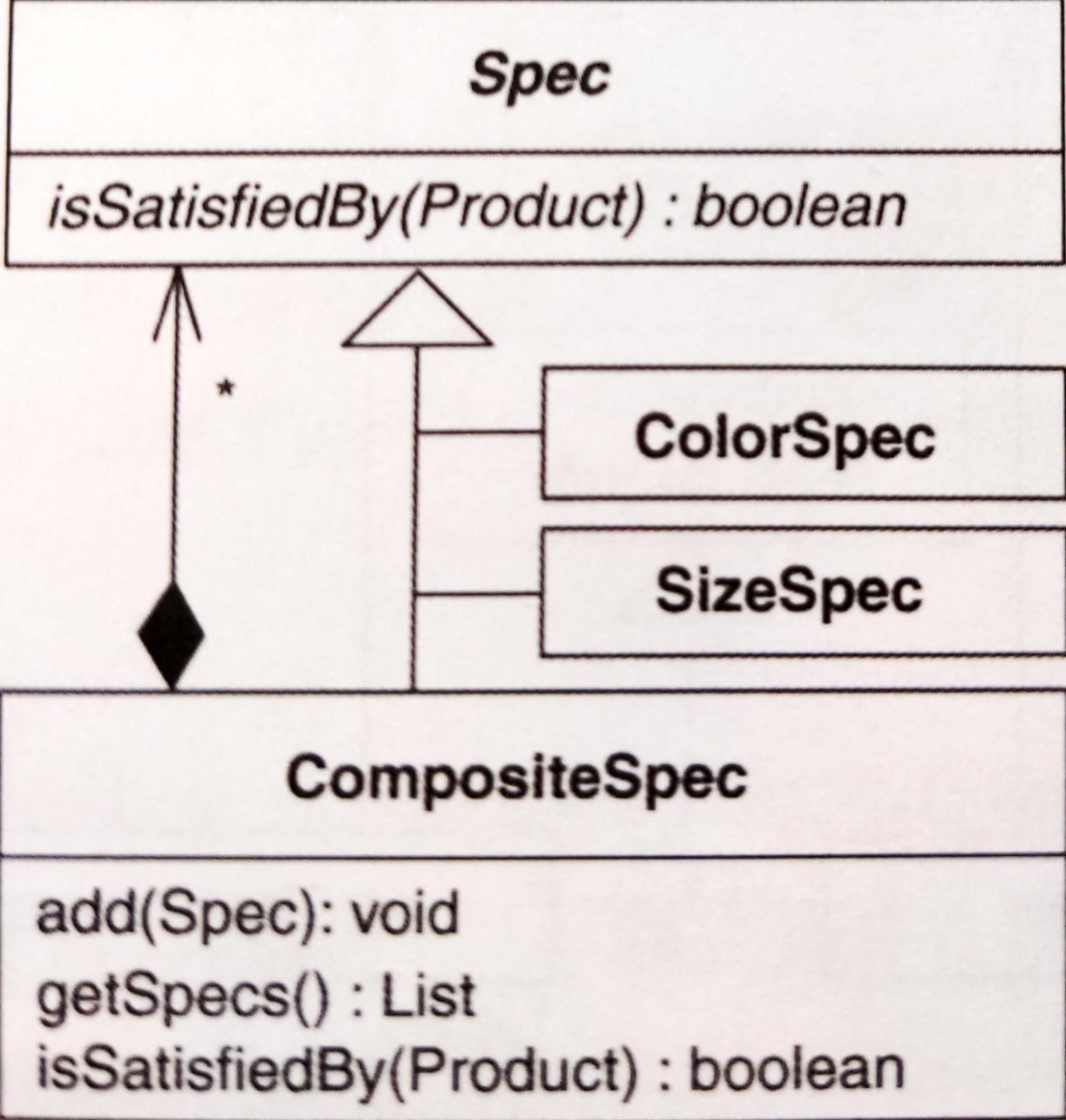
# Replace One/Many Distinctions with Composite
以 Composite 取代單/多差異,建立「能處理單物件和多物件」的程式碼。
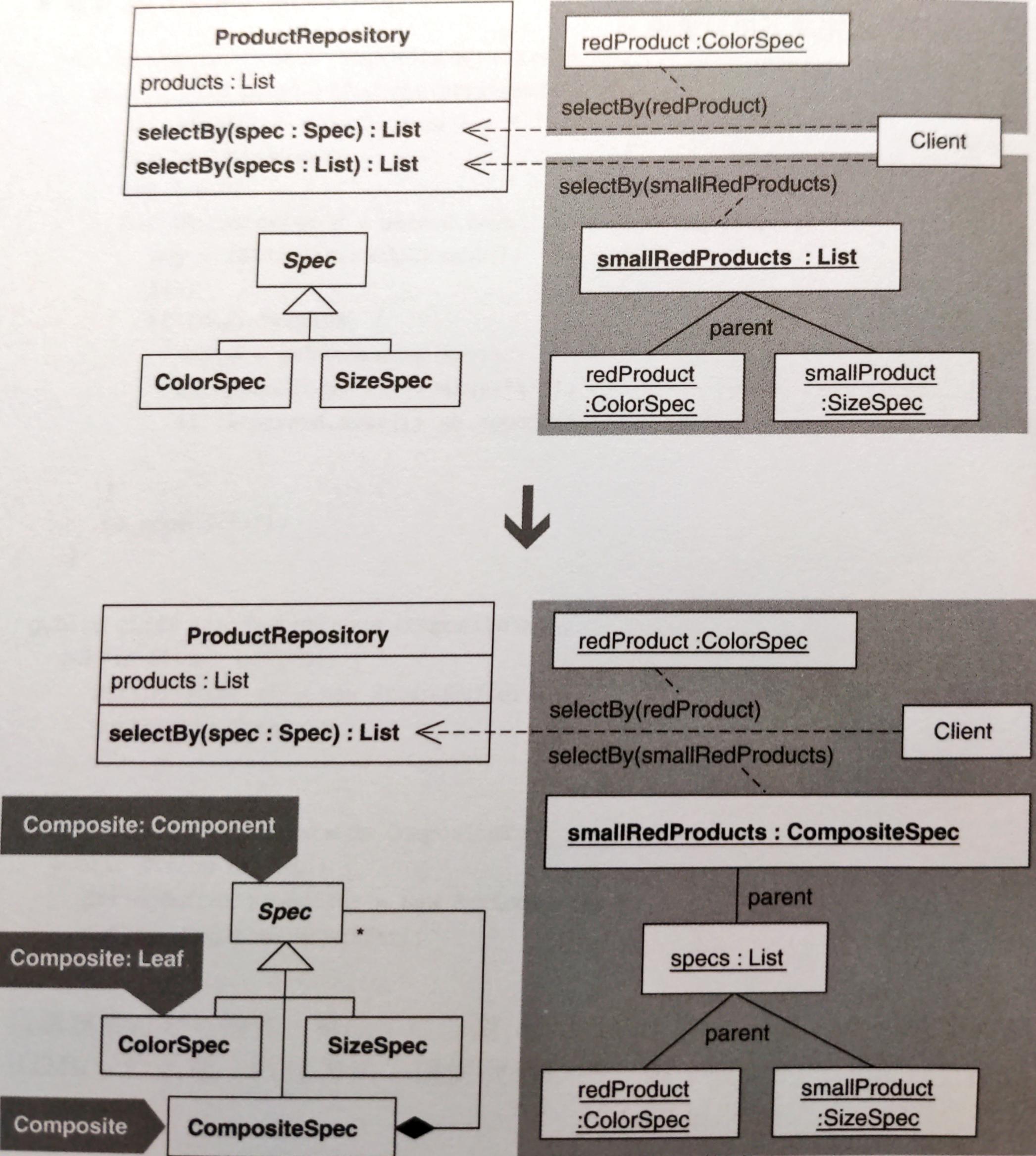
# 動機
當有個類別用來處理「單物件」的函式,又有一個用來處理「多物件」的函式,此時 one/many distinctions 便存在,造成:
重複碼
客戶碼不一致:兩個函式 signatures 不一樣,客戶碼寫法也就不一樣。
最後結果的合併 實例:假設你想找出價格低於 $5.00 的所有紅色商品,或價格高於 $10.00 的所有藍色商品,方法是呼叫
ProductRepository的selectBy(List specs),它會回傳型別為List的商品清單,如下:List redProductsUnderFiveDollars = new ArrayList(); redProductsUnderFiveDollars.add(new ColorSpec(Color.red)); redProductsUnderFiveDollars.add(new BelowPriceSpec(5.00)); List foundRedProductsUnderFiveDollars = productRepository.selectBy(redProductsUnderFiveDollars);1
2
3
4但是
selectBy(List specs)無法處理 OR 條件。因此必須分別呼叫再手動合併:List foundRedProductsUnderFiveDollars = productRepository.selectBy(redProductsUnderFiveDolla rs); List foundBlueProductsAboveTenDollars = productRepository.selectBy(blueProductsAboveTenDollars); List foundProducts = new ArrayList(); foundProducts.addAll(foundRedProductsUnderFiveDollars); foundProducts.addAll(foundBlueProductsAboveTenDollars);1
2
3
4
5
6
以 Composite 解決的好處:
- 沒有重複碼:因為只有一個函式,不管被處理的物件為一個或多個。
- 客戶端透過一致的方式與函式溝通。
- 客戶端透過一次呼叫就可以得到整個樹狀物件的處理結果:
缺點跟型別安全性 (type safety) 有關。為了防止客戶把無效物件加入 Composite,其程式碼必須在執行期檢查。
優點
- 將重複碼移除
- 處理單/多物件的方式一致
- 有叫豐富的多物件處理方式
缺點
- Composite 建構期間要在執行期檢查型別
# 作法
單物件處理函式:one-object method 多物件處理函式:many-object method
- many-object method 應該接受一個集合 (collection) 作為參數。
所以,
- 建立一個新類別,以 collection 為參數,並為此 collection 提供 getter。 此類別為 Composite。
- 在 many-object method 中為你的 composite 宣告並具現一個實體。
- 找出 many-object method 中對 collection 的所有引用點,改寫成讓它透過 composite 的 getter 函式來取得 collection。
- 找出 many-object method 中觸及 collection 的程式碼,實施 Extract Method。抽出來的函式設定為 public,再實施 Move Method 移到 composite 內。
- 現在 many-object method 和 one-object method 幾乎相同。主要差在前者具現出你的 composite。 如果還有其他不同,請以重構來消除。
- 修改 many-object method,讓它只包含一行程式碼:呼叫 one-object method 並將你的 composite 實體當作參數傳入。
你需要讓 composite 共享「one-object method 所使用的 interface 或 superclass」。
- 為此,考慮讓 composite 成為 one-object method 所用的型別的 subclass,或是用 Extract Interface 建立新的 interface,把 composite 和所有物件傳入 one-object method 的實作中。
- many-object method 現在只剩一行,可對它實施 Inline Method。
- 對你的 composite 實施 Encapsulate Collection。這會在 composite 產生一個
add(...)函式。 讓客戶端呼叫它,而不是把 collection 傳給 composite 的建構式。 現在 collection 的 getter 回傳一個不可變的 collection。
# 範例
先寫測試開始。
public class ProductRepositoryTest extends TestCase {
private ProductRepository repository;
private Product fireTruck = new Product("f1234", "Fire Truck", Color.red, 8.95f, ProductSize.MEDIUM);
private Product barbieClassic = new Product("b7654", "Barbie Classic", Color.yellow, 15.95f, ProductSize.SMALL);
private Product frisbee = new Product("f4321", "Frisbee", Color.pink, 9.99f, ProductSize.LARGE);
private Product baseball = new Product("b2343", "Baseball", Color.white, 8.95f, ProductSize.NOT_APPLICABLE);
private Product toyConvertible = new Product("p1112", "Toy Porsche Convertible", Color.red, 230.00f, ProductSize.NOT_APPLICABLE);
protected void setUp() {
repository = new ProductRepository();
repository.add(fireTruck);
repository.add(barbieClassic);
repository.add(frisbee);
repository.add(baseball);
repository.add(toyConvertible);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
第一個測試是呼叫 repository.selectBy(specs) 來找出某個顏色的 Product 實體:
public class ProductRepositoryTest extends TestCase {
public void testFindByColor() {
List foundProducts = repository.selectBy(new ColorSpec(Color.red));
assertEquals("found 2 red products", 2, foundProducts.size());
assertTrue("found fireTruck", foundProducts.contains(fireTruck));
assertTrue( "found Toy Porsche Convertible", foundProducts.contains(toyConvertible));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
函式 repository.selectBy(specs) 像這樣:
public class ProductRepository {
private List products = new ArrayList();
public Iterator iterator() {
return products.iterator();
}
public List selectBy(List specs) {
List foundProducts = new ArrayList();
Iterator products = iterator();
while (products.hasNext()) {
Product product = (Product)products.next();
if (spec.isSatisfiedBy(product ))
foundProducts.add(product);
}
return foundProducts;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
另一個測試,呼叫了不同的 repository.selectBy(specs) 函式。這個測試把 Spec 實體聚集在一個 List 中,為了從 repository 選出特定類型的產品:
public class ProductRepositoryTest extends TestCase {
// ...
public void testFindByColorSizeAndBelowPrice() {
List specs = new ArrayList();
specs.add(new ColorSpec(Color.red));
specs.add(new SizeSpec(ProductSize.SMALL));
specs.add(new BelowPriceSpec(10.00));
List foundProducts = repository.selectBy(specs);
assertEquals( "small red products below $10.00", 0, foundProducts.size());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
List-based repository.selectBy(specs) 看起來像這樣:
public class ProductRepository {
public List selectBy(List specs) {
List foundProducts = new ArrayList();
Iterator products = iterator();
while (products.hasNext()) {
Product product = (Product)products.next();
Iterator specifications = specs.iterator();
boolean satisfiesAllSpecs = true;
while (specifications.hasNext()) {
Spec productSpec = ((Spec)specifications.next());
satisfiesAllSpecs &= productSpec.isSatisfiedBy(product);
}
if (satisfiesAllSpecs)
foundProducts.add(product);
}
return foundProducts;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
List-based 的更複雜,且有很多個重複碼。使用 Composite 可以消除重複,有另一個方法可以消除重複而不使用 Composite:
public class ProductRepository {
public List selectBy(Spec spec) {
Spec[] specs = { spec };
return selectBy(Arrays.asList(specs));
}
public List selectBy(List specs) {
// ...
// same implementation as before
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
這個解法讓比較複雜的 List selectBy(List specs) 維持原樣,簡化了 one-Spec selectBy(...)。
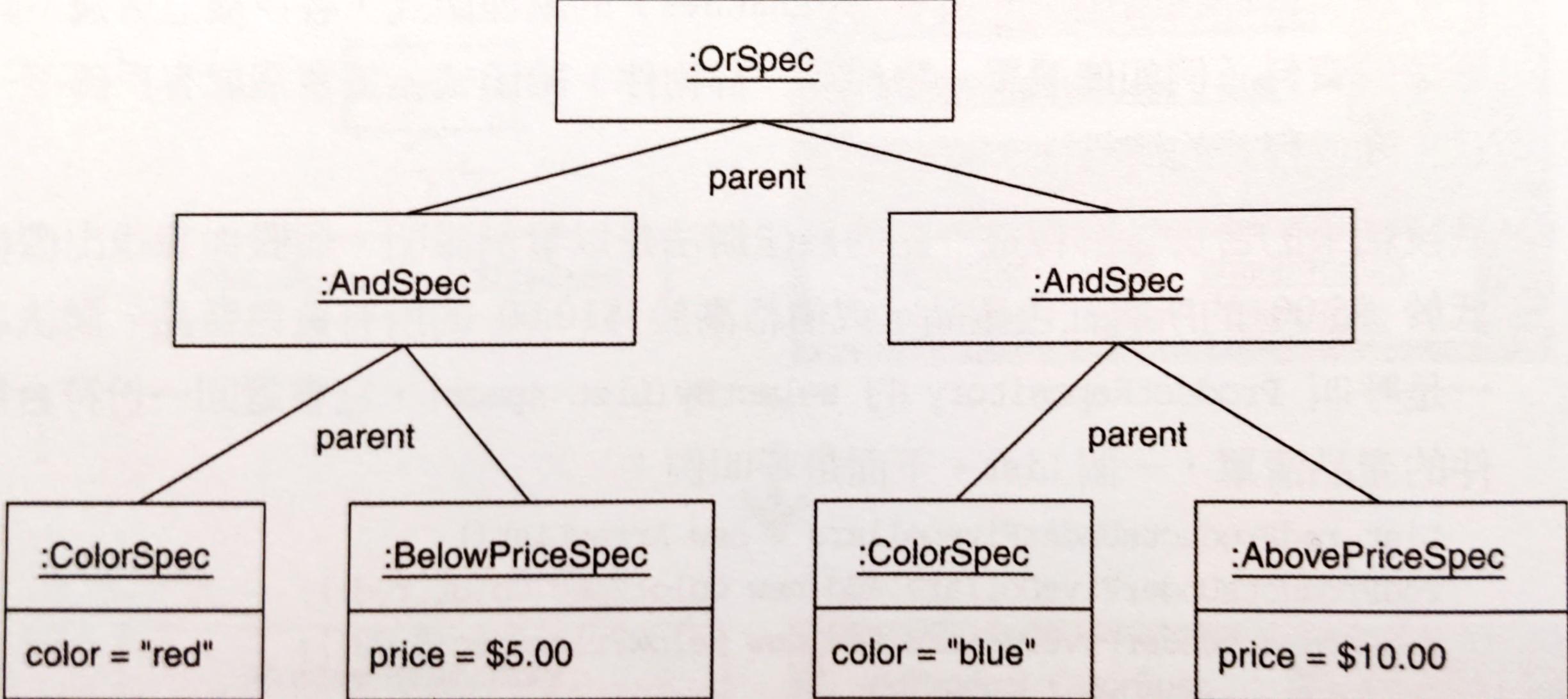
問題:以這個解法代替 refactor to Composite 是明智之舉嗎?這取決於需求。本例需要支援 OR, AND 和 NOT 條件查詢,像是:
product.getColor() != targetColor || product.getPrice() < targetPrice
List-based 無法支援上述查詢。此外我們寧願只有唯一一個 selectBy(...),讓客戶端可以使用一種方式來呼叫它。因此決定使用 refactor to Composite:
List-basedselectBy(...)是 many-object method,接受參數List specs。 先建立一個新的類別持有specs參數,並提供 getter:public class CompositeSpec { private List specs; public CompositeSpec(List specs) { this.specs = specs; } public List getSpecs() { return specs; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11接下來,在
List-basedselectBy(...)具現這個類別,並使程式碼改成呼叫 getter:public class ProductRepository { public List selectBy(List specs) { CompositeSpec spec = new CompositeSpec(specs); List foundProducts = new ArrayList(); Iterator products = iterator(); while (products.hasNext()) { Product product = (Product)products.next(); Iterator specifications = spec.getSpecs().iterator(); boolean satisfiesAllSpecs = true; while (specifications.hasNext()) { Spec productSpec = ((Spec)specifications.next()); satisfiesAllSpecs &= productSpec.isSatisfiedBy(product); } if (satisfiesAllSpecs) foundProducts.add(product); } return foundProducts; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20現在,對
selectBy(...)中「明確處理specs」的程式碼實施 Extract Method:public class ProductRepository { public List selectBy(List specs) { CompositeSpec spec = new CompositeSpec(specs); List foundProducts = new ArrayList(); Iterator products = iterator(); while (products.hasNext()) { Product product = (Product)products.next(); if (isSatisfiedBy(spec, product)) foundProducts.add(product); } return foundProducts; } public boolean isSatisfiedBy(CompositeSpec spec, Product product) { Iterator specifications = spec.getSpecs().iterator(); boolean satisfiesAllSpecs = true; while (specifications.hasNext()) { Spec productSpec = ((Spec)specifications.next()); satisfiesAllSpecs &= productSpec.isSatisfiedBy(product); } return satisfiesAllSpecs; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24通過編譯和測試以後,實施 Move Method 把
isSatisfiedBy(...)移到CompositeSpec內:public class ProductRepository { public List selectBy(List specs) { CompositeSpec spec = new CompositeSpec(specs); List foundProducts = new ArrayList(); Iterator products = iterator(); while (products.hasNext()) { Product product = (Product)products.next(); if (spec.isSatisfiedBy(product)) foundProducts.add(product); } return foundProducts; } public class CompositeSpec { public boolean isSatisfiedBy(Product product) { Iterator specifications = getSpecs().iterator(); boolean satisfiesAllSpecs = true; while (specifications.hasNext()) { Spec productSpec = ((Spec)specifications.next()); satisfiesAllSpecs &= productSpec.isSatisfiedBy(product); } return satisfiesAllSpecs; } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25現在,兩個
selectBy(...)幾乎一樣。唯一不同的是List-based 具現一個CompositeSpec實體:public class ProductRepository { public List selectBy(Spec spec) { // same code } public List selectBy(List specs) { CompositeSpec spec = new CompositeSpec(specs); // same code } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9現在我想讓
List-basedselectBy(...)呼叫 one-Spec selectBy(...):public class ProductRepository { public List selectBy(Spec spec) { // ... } public List selectBy(List specs) { return selectBy(new CompositeSpec(specs)); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8但無法順利編譯,因為
CompositeSpec沒有和Spec共用相同 interface,而Spec是在selectBy(Spec spec)會被用到。既然
CompositeSpec已經實作Spec宣告的isSatisfiedBy,那就順手讓CompositeSpec繼承Spec:public class CompositeSpec extends Spec ...1現在通過編譯。
List-basedselectBy(...)現在只有一行呼叫 one-Spec selectBy(...),所以可以實施 Inline Method。public class ProductRepositoryTest { public void testFindByColorSizeAndBelowPrice() { List specs = new ArrayList(); specs.add(new ColorSpec(Color.red)); specs.add(new SizeSpec(ProductSize.SMALL)); specs.add(new BelowPriceSpec(10.00)); // List foundProducts = repository.selectBy(specs); List foundProducts = repository.selectBy(new CompositeSpec(specs)); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10現在,只有一個
selectBy(...)接受像ColorSpecSizeSpec或新的CompositeSpec這樣的Spec物件。想建立 Composite 結構來支援邏輯運算,還需要NotSpec和OrSpec這樣的類別。在 Replace Implicit Language with Interpreter 這一章會描述如何產生這些類別。最後一步是對
CompositeSpec內的 collection 實施 Encapsulate Collection,來讓CompositeSpec更具型別安全性。首先定義
add(Spec spec):public class CompositeSpec extends Spec { private List specs; public void add(Spec spec) { specs.add(spec); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7初始化
specs:public class CompositeSpec extends Spec { private List specs = new ArrayList(); }1
2
3找出
CompositeSpec建構式所有呼叫者,讓他們改以呼叫新的CompositeSpecdefault 建構式和新的add(...)。public class ProductRepositoryTest { public void testFindByColorSizeAndBelowPrice() { // ... // List specs = new ArrayList(); CompositeSpec specs = new CompositeSpec(); specs.add(new ColorSpec(Color.red)); specs.add(new SizeSpec(ProductSize.SMALL)); specs.add(new BelowPriceSpec(10.00)); List foundProducts = repository.selectBy(specs); } // ... }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12現在沒人呼叫
CompositeSpec那個「接收一個List」的建構式了。因此把它移除:public class CompositeSpec extends Spec { // public CompositeSpec(List specs) { // this.specs = specs; // } }1
2
3
4
5現在,更新
CompositeSpec的getSpecs(...)使它回傳一個不可修改的specs:public class CompositeSpec extends Spec { private List specs = new ArrayList(); public List getSpecs() { return Collections.unmodifiableList (specs); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7