# Replace Conditional Logic with Strategy
以 Strategy 取代條件邏輯(Conditional Logic)。
為每個變體(variant)建立一個 Strategy 物件,然後將函式委派(delegate)給 Strategy 的實體。
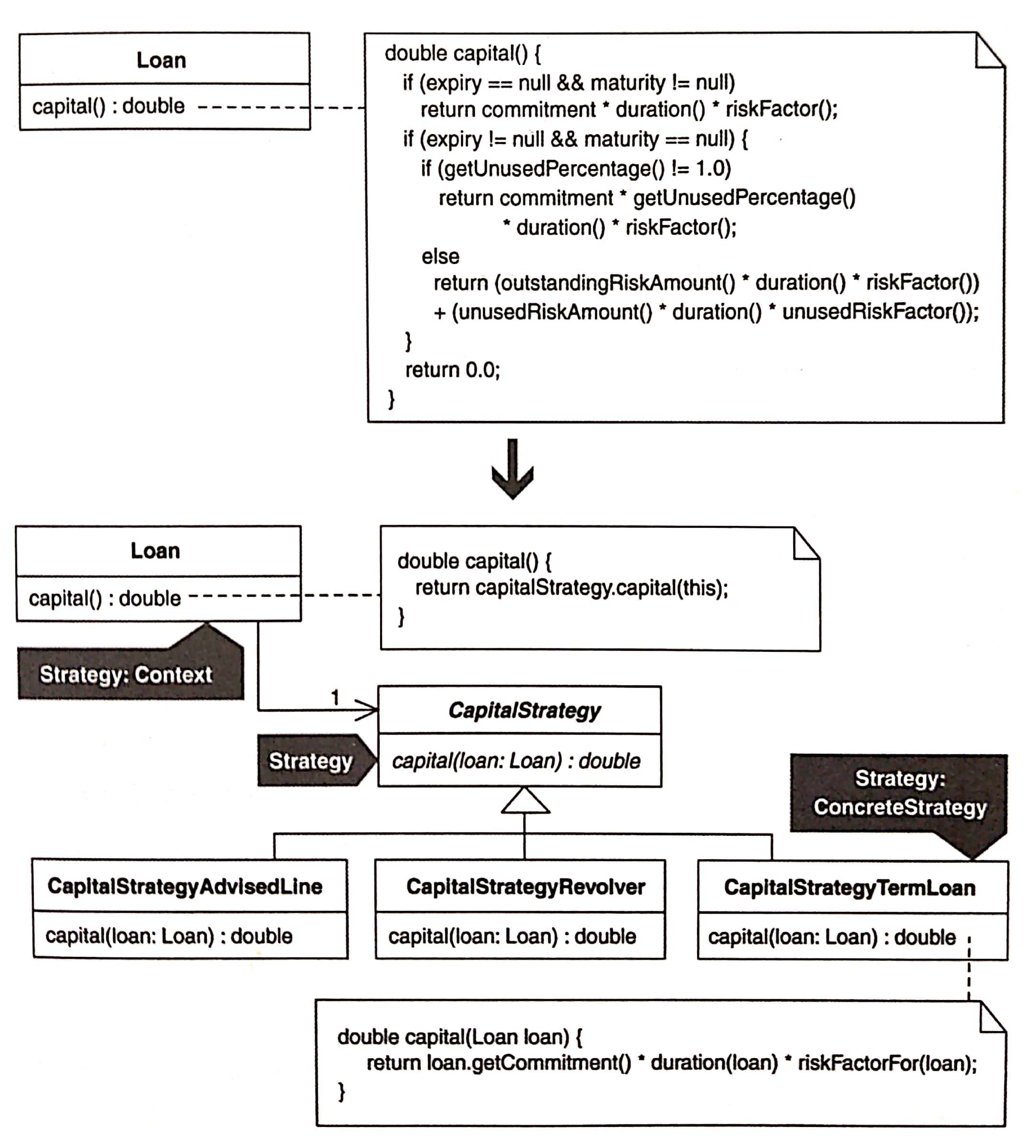
# 動機
優點
- 透過減少或移除條件邏輯的方式簡化
- 把演算法變異移給一個繼承體系,用來簡化類別
- 讓演算法可以在執行期轉換為另一個演算法
缺點
- 當「以繼承為基礎的解法」或來自 Simplifying Conditional Expression [F] 的解法更簡單時,會讓設計變得更複雜
- 會讓演算法從其 context class 中取資料的方式變得更複雜
# 作法
找出 context:帶有一個包含許多條件邏輯的計算方法(calculation method)。
建立一個 Strategy
以計算方法的行為為這個 Strategy 命名。使用 Move Method [F] 將計算方法移到 Strategy。
先在 context 上為這個計算方法保留一個簡易版本,context 會把實際工作委派給 Strategy。
為了實現這個委派,必須定義並具現一個 delegate 成為一個 context 的欄位,其 reference 指向 Strategy。 如果 Strategy 需要存取資料,以下有兩個常見作法:- 把 context 當作參數傳給 Strategy 的建構式或計算方法。
這麼做需要把 context 設定為 public。請考慮只給 context 的資料提供最少的公開權限。- 優點:為 context 新增新的 public 函式時,不用更動很多程式碼,就可以被所有 concrete Strategies 使用。
- 缺點:破壞資訊隱藏,本來只能給 context 看到的資料會讓其他類別看到。
- 透過計算方法的參數,將需要的傳進 Strategy。
- 優點:context 和 Strategy 之間形成最低耦合。
- 缺點:資料會被傳進 每個 concrete Strategy,不論它們是否需要這些資料。
這些方法所面臨的挑戰,與所需要的資料量有關。如果參數太多,最好就把整個 context 以 reference 傳給 Strategy。也可以用 Introduce Parameter Object [F] 減少參數量。如果某些參數只為了某個特定的 concrete Strategy 需要,可以從參數列移除,改成透過建構式傳入。
Context 中可能會有些輔助函式應該在 Strategy 上面,可以實作任何必要的 accessors,讓它將輔助函式從 context 移到 Strategy。
- 把 context 當作參數傳給 Strategy 的建構式或計算方法。
讓客戶碼裝配 context,使它帶有 Strategy 實體。
作法是對 context 程式碼中「具現一個 concrete Strategy 並作為委派對象」的部份實施 Extract Parameter [F]。在 Strategy 計算方法上面使用 Replace Conditional with Polymorphism [F]。
為了這麼做,你必須使用 Replace Type Code with Subclasses [F] 或是 Replace Type Code with State/Strategy [F],請選擇前者。如果計算方法上的條件邏輯辨識出特定計算型別,請使用條件邏輯代替顯式型別(explicit types)。一次只集中焦點建立一個 subclass。如果可以的話,請將 Strategy 變成 abstract class。
# 範例
範例是一個三種貸款的資金計算程式:
- 定期貸款(term loan)
- 循環信用貸款(revolver)
- 通知額度貸款(advised line)
Loan 需要完成下列事項:
- 針對各種貸款多樣化計算資金。
如果每種資金計算方式都要有一個Loansubclass,那麼Loan會負擔過多 subclasses,如下圖:
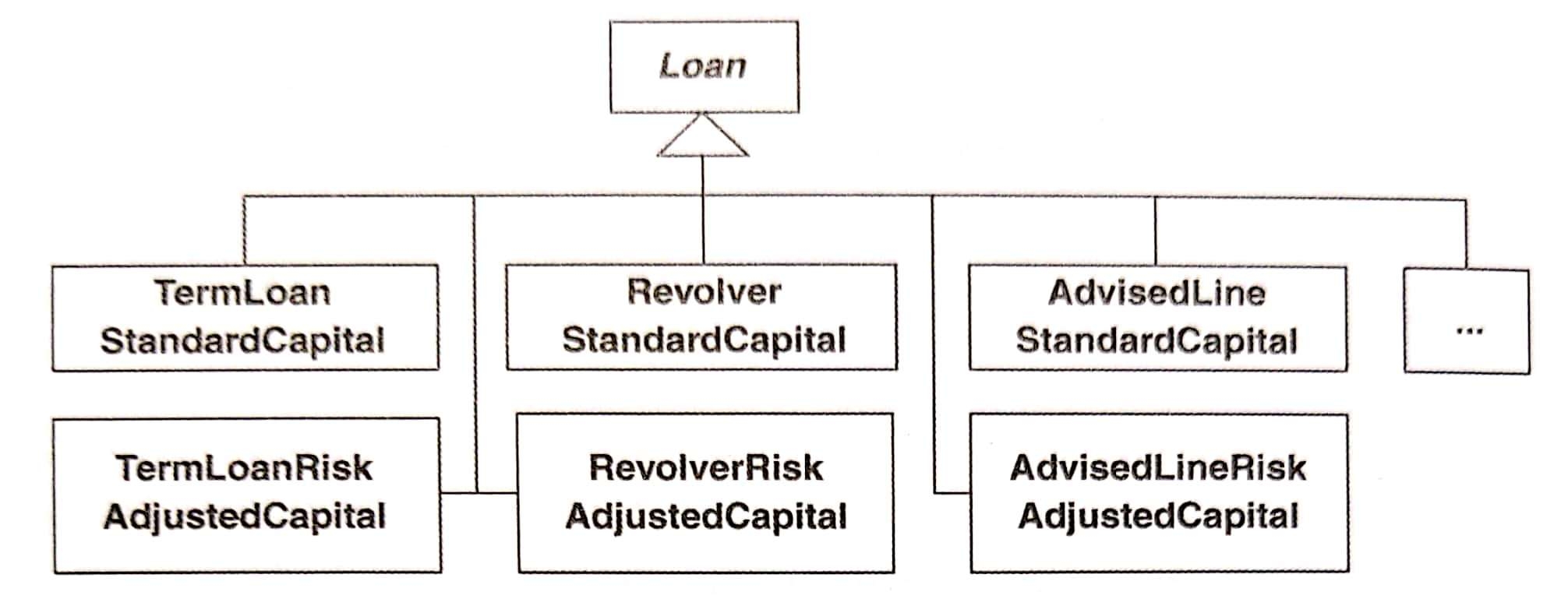
- 在執行期間改變資金計算方式,但不改變
Loan實體的 class 型別。
「交換Loan物件的 Strategy 實體使成為另一個 Strategy 實體」比「改變整個Loan物件使它從某個Loansubclass 改變成另一個Loansubclass」更容易達成。
先找出 context: 在 Loan 類別中,有一個 capital() 的計算方法。
public class Loan {
// ...
public double capital() {
if (expiry == null && maturity != null) // 1
return commitment * duration() * riskFactor();
if (expiry != null && maturity == null) {
if (getUnusedPercentage() != 1.0) // 2
return commitment * getUnusedPercentage() * duration() * riskFactor();
else // 3
return (outstandingRiskAmount() * duration() * riskFactor()) + (unusedRiskAmount() * duration() * unusedRiskFactor());
}
return 0.0; // 4
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
內含以下幾個輔助函式:
public class Loan {
// ...
private double outstandingRiskAmount() {
return outstanding;
}
private double unusedRiskAmount() {
return (commitment - outstanding);
}
public double duration() {
if (expiry == null && maturity != null)
return weightedAverageDuration();
else if (expiry != null && maturity == null)
return yearsTo(expiry);
return 0.0;
}
private double weightedAverageDuration() {
double duration = 0.0;
double weightedAverage = 0.0;
double sumOfPayments = 0.0;
Iterator loanPayments = payments.iterator();
while (loanPayments.hasNext()) {
Payment payment = (Payment)loanPayments.next();
sumOfPayments += payment.amount();
weightedAverage += yearsTo(payment.date()) * payment.amount();
}
if (commitment != 0.0)
duration = weightedAverage / sumOfPayments;
return duration;
}
private double yearsTo(Date endDate) {
Date beginDate = (today == null ? start : today);
return ((endDate.getTime() - beginDate.getTime()) / MILLIS_PER_DAY) / DAYS_PER_YEAR;
}
private double riskFactor() {
return RiskFactor.getFactors().forRating(riskRating);
}
private double unusedRiskFactor() {
return UnusedRiskFactors.getFactors().forRating( riskRating);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
建立一個
CapitalStrategy類別public class CapitalStrategy { }1
2
3用 Move Method [F] 把
capital()計算工作移到CapitalStrategy。這個步驟需要在Loan上留下一個簡單版的capital(),用來把工作委派給一個CapitalStrategy的實體。首先宣告一個
capital():public class CapitalStrategy { public double capital() { return 0.0; } }1
2
3
4
5然後從
Loan複製程式碼到CapitalStrategy:public class CapitalStrategy { public double capital() { // copied from Loan if (expiry == null && maturity != null) return commitment * duration() * riskFactor(); if (expiry != null && maturity == null) { if (getUnusedPercentage() != 1.0) return commitment * getUnusedPercentage() * duration() * riskFactor(); else return (outstandingRiskAmount() * duration() * riskFactor()) + (unusedRiskAmount() * duration() * unusedRiskFactor()); } return 0.0; } private double riskFactor() { // moved from Loan return RiskFactor.getFactors().forRating(riskRating); } private double unusedRiskFactor() { // moved from Loan return UnusedRiskFactors.getFactors().forRating(riskRating); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19這時候發現,不能把
duration()移到CapitalStrategy,因為weightedAverageDuration也需要知道Loan的付款資訊。一旦我們讓CapitalStrategy可以取用付款資訊,就能夠把duration()和它的輔助函式移到CapitalStrategy。很快的我就會做這件事。現在我們需要編譯被我複製到
CapitalStrategy的程式碼,為此我們必須決定:- 要把
Loanreference 當作參數傳給capital()和它的輔助函式 - 把資料當作參數傳給
capital(),讓capital()可以使用它們並且繼續傳給它的輔助函式
capital()需要以下這些來自Loan實體的訊息:- Expiry date
- Maturity date
- Duration
- Commitment amount
- Risk rating
- Unused percentage
- Outstanding risk amount
- Unused risk amount
如果能夠縮減這列表,就能使用資料傳遞法。
因此推測我們可以建立一個LoanRangeclass 來儲存與Loan實體相關的日期。
或許還能把 Commitment amount、Outstanding risk amount 和 Unused risk amount 組成一個LoanRiskclass。
但我們還有其他函式需要從Loan移到CapitalStrategy(e.g.duraion()),就放棄上面的想法。因為搬動那些函式需要更多的資訊給CapitalStrategy。
因此,我們決定只傳遞Loanreference 給CapitalStrategy。public class CapitalStrategy { public double capital(Loan loan ) { if ( loan.getExpiry() == null && loan.getMaturity() != null) return loan.getCommitment() * loan .duration() * riskFactorFor(loan) ; if ( loan.getExpiry() != null && loan.getMaturity() == null) { if (loan.getUnusedPercentage() != 1.0) return loan.getCommitment() * loan.getUnusedPercentage() * loan. duration() * riskFactorFor(loan) ; else return (loan.outstandingRiskAmount() * loan.duration() * riskFactorFor(loan) ) + ( loan.unusedRiskAmount() * loan.duration() * unusedRiskFactorFor(loan) ); } return 0.0; } private double riskFactorFor(Loan loan) { return RiskFactor.getFactors().forRating( loan.getRiskRating() ); } private double unusedRiskFactorFor(Loan loan) { return UnusedRiskFactors.getFactors().forRating(loan.getRiskRating()); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21為此需要對
Loan進行一些改動來取得資料:public class Loan { Date getExpiry() { return expiry; } Date getMaturity() { return maturity; } double getCommitment() { return commitment; } double getUnusedPercentage() { return unusedPercentage; } // private double outstandingRiskAmount() { return outstanding; } // private double unusedRiskAmount() { return (commitment - outstanding); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23Move Method 下一步是讓
Loan把資金計算的工作委託給CapitalStrategy:public class Loan { public double capital() { return new CapitalStrategy().capital(this); } }1
2
3
4
5執行以下測試,檢查是否可以正常運作:
public class CapitalCalculationTests extends TestCase { public void testTermLoanSamePayments() { Date start = november(20, 2003); Date maturity = november(20, 2006); Loan termLoan = Loan.newTermLoan(LOAN_AMOUNT, start, maturity, HIGH_RISK_RATING); termLoan.payment(1000.00, november(20, 2004)); termLoan.payment(1000.00, november(20, 2005)); termLoan.payment(1000.00, november(20, 2006)); assertEquals("duration", 2.0, termLoan.duration(), TWO_DIGIT_PRECISION); assertEquals("capital", 210.00, termLoan.capital(), TWO_DIGIT_PRECISION); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12通過測試以後,現在可以集中精力在資金計算相關特性從
Loan移到CapitalStrategy,完成後如下:public class CapitalStrategy { private static final int MILLIS_PER_DAY = 86400000; private static final int DAYS_PER_YEAR = 365; public double capital(Loan loan) { if (loan.getExpiry() == null && loan.getMaturity() != null) return loan.getCommitment() * loan.duration() * riskFactorFor(loan); if (loan.getExpiry() != null && loan.getMaturity() == null) { if (loan.getUnusedPercentage() != 1.0) return loan.getCommitment() * loan.getUnusedPercentage() * loan.duration() * riskFactorFor(loan); else return (loan.outstandingRiskAmount() * loan.duration() * riskFactorFor(loan)) + (loan.unusedRiskAmount() * loan.duration() * unusedRiskFactorFor(loan)); } return 0.0; } private double riskFactorFor(Loan loan) { return RiskFactor.getFactors().forRating(loan.getRiskRating()); } private double unusedRiskFactorFor(Loan loan) { return UnusedRiskFactors.getFactors().forRating(loan.getRiskRating()); } public double duration(Loan loan) { if (loan.getExpiry() == null && loan.getMaturity() != null) return weightedAverageDuration(loan); else if (loan.getExpiry() != null && loan.getMaturity() == null) return yearsTo(loan.getExpiry(), loan); return 0.0; } private double weightedAverageDuration(Loan loan) { double duration = 0.0; double weightedAverage = 0.0; double sumOfPayments = 0.0; Iterator loanPayments = loan.getPayments().iterator(); while (loanPayments.hasNext()) { Payment payment = (Payment)loanPayments.next(); sumOfPayments += payment.amount(); weightedAverage += yearsTo(payment.date(), loan) * payment.amount(); } if (loan.getCommitment() != 0.0) duration = weightedAverage / sumOfPayments; return duration; } private double yearsTo(Date endDate, Loan loan) { Date beginDate = (loan.getToday() == null ? loan.getStart() : loan.getToday()); return ((endDate.getTime() - beginDate.getTime()) / MILLIS_PER_DAY) / DAYS_PER_YEAR; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48在改動過後,
Loan的資金和週期計算看起來像這樣:public class Loan { public double capital() { return new CapitalStrategy().capital(this); } public double duration() { return new CapitalStrategy().duration(this); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8雖說不打算太早對
Loanclass 進行最佳化,但我們不放棄移除重複碼的機會。應該以Loan的CapitalStrategy欄位取代上面的new CapitalStrategy()...:public class Loan { private CapitalStrategy capitalStrategy; private Loan(double commitment, double outstanding, Date start, Date expiry, Date maturity, int riskRating) { capitalStrategy = new CapitalStrategy(); //... } public double capital() { return capitalStrategy.capital(this); } public double duration() { return capitalStrategy.duration(this); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13到目前為止實現了 Move Method。
- 要把
接下來實施 Extract Parameter 來設定委託值,在以下的
new CapitalStrategy()地方。目前它是寫死的(hard-coded)。public class Loan { private Loan(..., CapitalStrategy capitalStrategy ) { // ... this.capitalStrategy = capitalStrategy; } public static Loan newTermLoan(double commitment, Date start, Date maturity, int riskRating) { return new Loan(commitment, commitment, start, null, maturity, riskRating, new CapitalStrategy()); } public static Loan newRevolver(double commitment, Date start, Date expiry, int riskRating) { return new Loan(commitment, 0, start, expiry, null, riskRating, new CapitalStrategy()); } public static Loan newAdvisedLine(double commitment, Date start, Date expiry, int riskRating) { if (riskRating > 3) return null; Loan advisedLine = new Loan(commitment, 0, start, expiry, null, riskRating, new CapitalStrategy()); advisedLine.setUnusedPercentage(0.1); return advisedLine; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19在
CapitalStrategy的capital()實施 Replace Conditional with Polymorphism。第一步是產生一個計算定期貸款資金的 subclass。這意味著讓CapitalStrategy(以下未列出的)幾個函式成為 protected,並將幾個函式移到CapitalStrategyTermLoan的新 class 中,如下:public class CapitalStrategyTermLoan extends CapitalStrategy { public double capital(Loan loan) { return loan.getCommitment() * duration(loan) * riskFactorFor(loan); } public double duration(Loan loan) { return weightedAverageDuration(loan); } private double weightedAverageDuration(Loan loan) { double duration = 0.0; double weightedAverage = 0.0; double sumOfPayments = 0.0; Iterator loanPayments = loan.getPayments().iterator(); while (loanPayments.hasNext()) { Payment payment = (Payment)loanPayments.next(); sumOfPayments += payment.amount(); weightedAverage += yearsTo(payment.date(), loan) * payment.amount(); } if (loan.getCommitment() != 0.0) duration = weightedAverage / sumOfPayments; return duration; }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26為了測試它,我們要更新
Loan如下:public class Loan { public static Loan newTermLoan( double commitment, Date start, Date maturity, int riskRating) { return new Loan( commitment, commitment, start, null, maturity, riskRating, new CapitalStrategyTermLoan() ); } }1
2
3
4
5測試通過以後,繼續實施 Replace Conditional with Polymorphism 建立另外兩種貸款類型:循環信用貸款(revolver)和通知額度(advised line) 的資金計算策略。
public class Loan { public static Loan newRevolver( double commitment, Date start, Date expiry, int riskRating) { return new Loan( commitment, 0, start, expiry, null, riskRating, new CapitalStrategyRevolver() ); } public static Loan newAdvisedLine( double commitment, Date start, Date expiry, int riskRating) { if (riskRating > 3) return null; Loan advisedLine = new Loan( commitment, 0, start, expiry, null, riskRating, new CapitalStrategyAdvisedLine()); advisedLine.setUnusedPercentage(0.1); return advisedLine; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13下圖是所有 Strategy 的 classes:
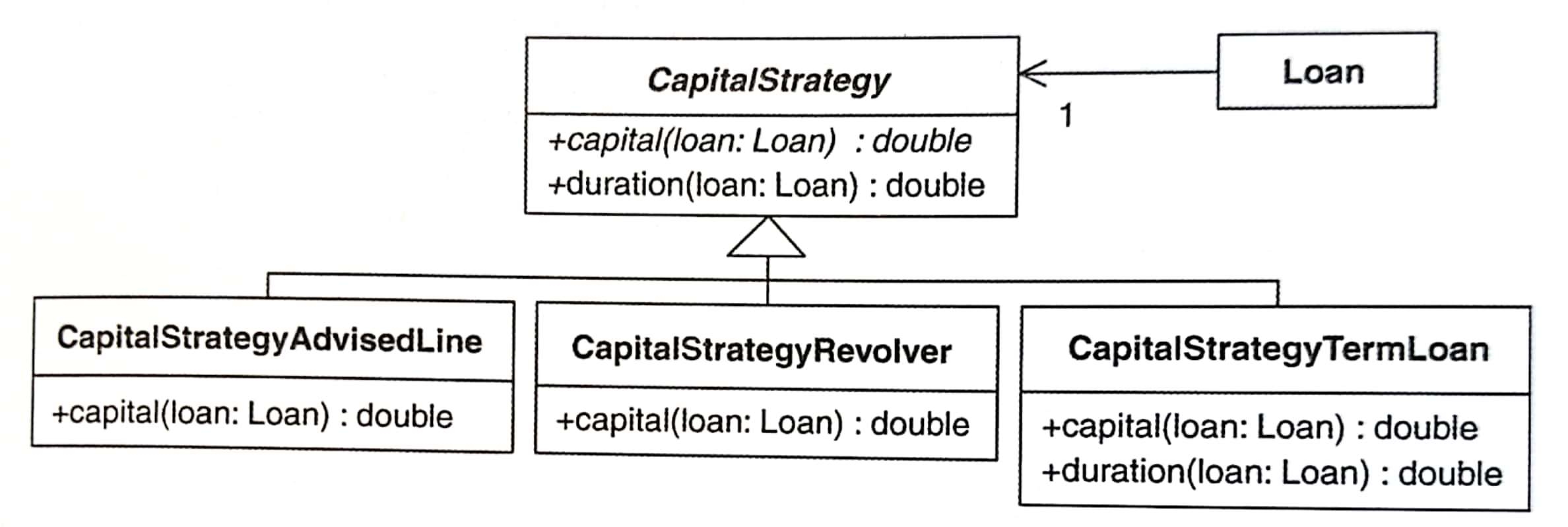
CapitalStrategyclass 現在是個 abstract class:public abstract class CapitalStrategy { private static final int MILLIS_PER_DAY = 86400000; private static final int DAYS_PER_YEAR = 365; public abstract double capital(Loan loan); protected double riskFactorFor(Loan loan) { return RiskFactor.getFactors().forRating(loan.getRiskRating()); } public double duration(Loan loan) { return yearsTo(loan.getExpiry(), loan); } protected double yearsTo(Date endDate, Loan loan) { Date beginDate = (loan.getToday() == null ? loan.getStart() : loan.getToday()); return ((endDate.getTime() - beginDate.getTime()) / MILLIS_PER_DAY) / DAYS_PER_YEAR; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15完成重構以後,現在資金計算改成以 concrete Strategy 執行。